What Causes Heart Disease?
Heart disease can be defined as “any disorder that affects the heart. The term “heart disease” may be used incorrectly (as a synonym for coronary artery disease). Heart disease is synonymous with cardiac disease but not with cardiovascular disease which is any disease of the heart or blood vessels”. The heart is a muscular organ that requires blood to supply oxygen and nutrients for it to function; the coronary arteries are the vessels that supply the blood.
Common Types of Heart Disease
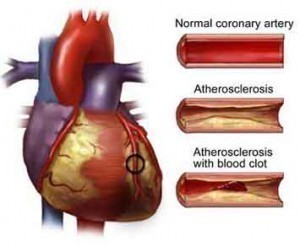
- Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the most common type and leading cause of heart attacks. The coronary arteries narrow (atherosclerosis) as cholesterol builds up inside the artery. If the arteries become too narrow and hard, blood supply to the heart muscle may be slowed down causing pain, or angina.
- As mentioned before Angina is pain or discomfort that occurs when the heart does not get enough blood. The pain commonly materializes as a squeezing or pressing pressure in the chest and may also occur in the shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back. Angina is not a heart attack, but having angina may lead to one.
- Heart attack or myocardial infarction occurs when an artery is severely or completely blocked. When a plaque ruptures, blood clot forms completely obstructing the artery and stops blood flow to part of the heart muscle, which eventually dies.
- Heart failure occurs when the heart is not able to pump blood through the body as well as it should. This means that other organs which normally get blood from the heart, do not get enough blood.
- Heart arrhythmias are changes in the beat of the heart which are harmless in most cases. Arrhythmias are more common in older people.
Causes of Heart Disease
- Coronary artery disease (CAD) – research shows that CAD starts when certain factors such as smoking and high blood pressure damage the inner layers of the coronary arteries resulting in atherosclerosis ; other factors include high intake of certain fats and cholesterol in the blood and high amounts of sugar in the blood due to insulin resistance or diabetes, obesity and inactivity.
- Arrhythmias – conditions that can lead to arrhythmias are CAD, high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, excess alcohol or caffeine, drug abuse, stress, congenital heart defects (resulting from medical conditions, medications and genes) and prescribed or over-the-counter medications.
- Heart Attack – can occur due to a condition called microvascular disease (when very small branches of arteries throughout the body become damaged), believed to be more common in women than men. A lesser cause is severe tightening of a coronary artery which may be due to drugs such as cocaine, emotional stress or pain, exposure to extreme cold and smoking.
- Heart Failure – CAD, heart attack, high blood pressure, abnormal heart valves, diabetes, and severe lung disease are some of the factors that increase your risk of a heart failure. Smoking, obesity, eating foods high in fat and cholesterol and physical inactivity can also contribute to heart failure.
For more information on What Causes Heart Disease read: