Abdominal Hernia Symptoms
Abdominal hernia is a condition characterized with a muscle defect in the abdominal wall resulting to a gap or hole in the abdominal cavity. This allows pressure on the abdominal organs such as intestines as well as fats to be pushed out of the abdominal cavity. While some abdominal hernia symptoms are minor and sometimes asymptomatic on its early stage, the condition can become a medical emergency once the blood supply is cut off from the hernia opening. The abdominal hernia symptoms become a major condition that often requires surgery.
There are different types of abdominal hernia with its own symptoms to manifest. Among the common types are inguinal hernias occurring in the groin area, femoral hernia, incisional hernia, umbilical hernia, Spigelian hernia, epigastric hernia, and obturator hernia. Recognition of abdominal hernia symptoms are important when seeking medical intervention and to provide relief of its symptoms and potential risks.
Abdominal Hernia Symptoms and Signs
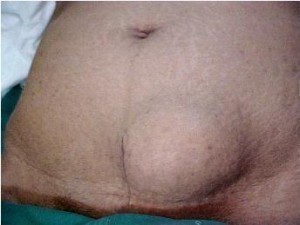
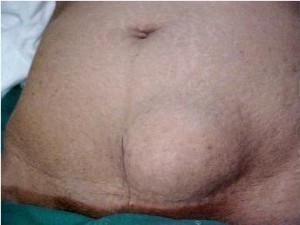
Abdominal hernia symptoms are manifested primarily with a bulge oftentimes represented with a localized swelling on the area on the abdomen where the hernia occurs. The abdominal hernia symptoms in mild cases are often unrecognizable and often times remain to be asymptomatic.
However, during physical exertion and activities such as lifting, exercise, coughing and other movements that subject the abdomen to increased pressure, the abdominal contents are further pushed into the gap of the abdominal cavity thereby increasing the size of the bulge.
Pain is another abdominal hernia symptom with different characteristics from dull, sharp or burning. The pain may be due to torn or stretched tissues or nerve irritation. The pain may be localized which is confined in one area or referred to other distant areas than the source of lesion. Nausea and vomiting are also experienced along with constipation and urinary symptoms.
Impotence is also common among males with abdominal hernia. In females, dyspareunia or painful intercourse is also an abdominal hernia symptom. Oftentimes there is marked inflammation along the bulge area.
Abdominal Hernia Symptoms Diagnosis
Most of the time, physical examination warrants a significant diagnosis for abdominal hernia to be established. It suffice for a medical practitioner to assess the patient’s symptoms based on physical examination by feeling for a bulge along the abdominal area when asking the patient to exert pressure on the abdominal muscles such as straining or coughing. This makes a simple palpitation and physical examination a simple diagnostic procedure to indicate abdominal hernia symptoms.
Abdominal Hernia Treatment
Because there is a high risk for an abdominal hernia to increase in size when left untreated, immediate intervention is necessary to address the potential risks and reduce an escalated abdominal hernia symptoms to progress. It is important to provide control on the hernia to increase in size and in minor abdominal hernia a truss or bandage can serve as support garment to prevent further protrusion of the hernia.
In both minor and major hernias, the person needs to avoid strenuous activities especially activities that can increase the abdominal pressure such as lifting and straining. Because the hernia can no longer be pushed back into its original place, surgery becomes a necessary treatment option. The procedure consists of sewing back the muscular cavity after the hernia has been pushed back into place.
It is vital to correct the abdominal hernia symptoms immediately as it can lead to further complications such as cutting down of blood supply to the intestine that can lead to an emergency condition.