Chronic Kidney Disease
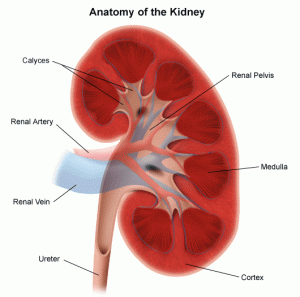
Kidneys are a pair of vital organs that are located at the rear of the abdominal cavity. These bean-shaped organs have numerous funtions that are extremely important for the proper functioning of the human body. They filter the blood and remove wastes that have been directed into the urinary bladder. Other functions of the kidneys include regulation of blood pressure and electrolytes and maintenance of acid-base balance. They also take care of the reabsorption of amino acids, glucose and water.
What is Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)?
Chronic Kidney Disease results in the progressive loss of renal function. This kidney failure usually occurs gradually, over a period of months to years. The loss or impairment of the kidney function leads to several complications such as the accumulation of substances that are excreted by the kidneys (toxic substances, waste, water). It could also lead to other diseases like anemia, increase in the acidity levels in the body fluids, bone related diseases and disorders with regard to fatty acids and cholesterol.
Symptoms of Chronic Kidney Disease
The symptoms of CKD tend to be very subtle. The following includes a list of possible symptoms of CKD:
- fatigue or feeling weak due to the accumulation of waste substances in the body that are normally removed by the kidney
- vomiting, nausea and general loss of appetite
- shortness of breath as a result of the accumulation of fluids in the lungs
- high blood pressure
- frequent need to urinate
- pain in the chest due to pericarditis (inflammation of the heart)
- bone related problem
Causes of Chronic Kidney Disease
Some of the causes that lead to Chronic Kidney Disease are:
- blood pressure
- diabetes
- polycystic kidney disease (both kidneys have multiple cysts)
- regular use of certain analgesics
- hardening or clogging of certain arteries that lead to the kidney (atherosclerosis)
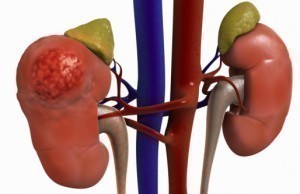
- certain cancers
- infections
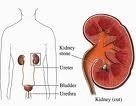
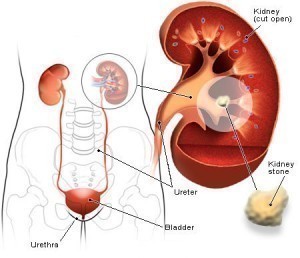
- presence of kidney stones
Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease
In order to treat Chronic Kidney Disease you will need to consult a professional medical practitioner. The treatment given will vary depending on the severity of the patient’s condition. However, the following pointers will definitely aid in making the treatment, more effective.
Restricting salt consumption: reduction of salt consumption to 4-6 grams a day will help control blood pressure and also help to avoid fluid retention in the body.
Restricting intake of water: Reduce your intake of water. Your medical practitioner will advice you regarding how much water can be consumed by you in a day. Ensure that you stick to the limit stipulated by your doctor.
Restriction of Potassium, Phosphorus, Protein: In the case of patients in their advanced stage of kidney disease, it is important to restrict the Potassium level in the body because the kidneys will not be able to remove Potassium. This could lead to an abnormality in the heart. It is best to avoid foods such as bananas that are a rich source of Potassium. A decrease in the Phophorus intake is recommended in order to protect the bones. Dairy products, eggs and soft drinks are some examples of the foods with high Phosphorus content. A decrease in protein intake can also aid in slowing the progress of the kidney disease.
Avoid taking certain analgesics: Consult a doctor with regard to this and avoid taking certain analgesics that are prone to worsen the kidney disease.
If the patient is a diabetic, has high blood pressure or cholesterol, he / she should continue to take all medications as directed by their medical practitioner. It also helps to lose excess body weight. If the patient smokes, it is best to take professional help and quit smoking. In the advanced stages of Chronic Kidney Disease when there is a nearly total loss of the kidney function, the patient will have to undergo renal replacement therapy in the form of either a kidney transplant or dialysis.
For more information on Chronic Kidney Disease read: