Coronary Artery Disease
Definition of Coronary Artery Disease
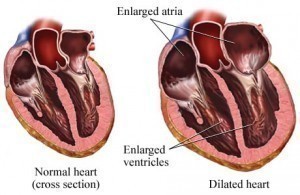
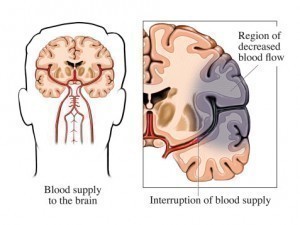
Coronary artery disease (CAD) occurs when the arteries and blood vessels that supply the heart with blood and oxygen begin to narrow affecting the functioning of the heart . This develops as a result of an accumulation of plaque in the arteries and blood vessels. If the blood flow is totally obstructed by plaque it can lead to a myocardial infarction or heart attack or in more tragic circumstances cardiac arrest. It is the leading cause of death in the United States of America and several other western countries.
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary Artery disease will manifest once the condition atherosclerosis develops within the heart’s vessels. The development of atherosclerosis then subsequent heart disease usually occurs as a result of certain factors. These factors may heighten an individual’s chance of developing the disease. The risk factors may include some of the following:
- Being obese or generously overweight
- A family history or genetic predisposition to developing this disease.
- Not engaging in physical activity, particularly exercise.
- Suffering from high blood pressure or hypertension.
- Being diabetic.
- Advanced age specifically being 40 years or older.
- Smoking.
- Having high levels of bad cholesterol and inadequate levels of good cholesterol.
- Being menopausal.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
It is not uncommon for the disease to be asymptomatic in the first phase of development. However once the disease progresses to the point where the heart has deteriorated some symptoms will become significantly evident. These may include the following:
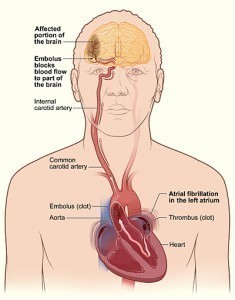
- Cardiac arrest, which will occur generally after a previous heart attack but may manifest as an early symptom.
- A feeling of dizziness and lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations that may be described as the sudden recognition of the beating heart in the chest, accompanied by the feeling that the heart is skipping beats.
- Angina pectoris or chest pain which will discontinue when resting and may be provoked by cold air.
- An overall feeling of discomfort.
- Shortness of breath that will generally occur after physical activity or when lying flat.
- An inability to sleep without being elevated by two pillows or more.
- An irregular heartbeat.
- Feeling some amount of weakness after activity.
- Pain in the jaw, left arm and shoulder blades that is felt after exercise or when resting.
- Fainting
Most symptoms will materialize after some kind of physical activity most frequently exercise. Because the need for oxygen and nutrients is not adequately fulfilled by the impeded blood vessels it will consequently progress into the presentation of the symptoms mentioned.
Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease
Treatment will include the use of medications in less drastic cases. For example antianginal drugs will be administered to lessen the intensity of angina attacks. In more unfavourable cases surgery may be required and may include, angioplasty, heart bypass surgery and minimally invasive heart surgery. A significant part of treatment will necessitate alterations to lifestyle such as consuming a healthy and nutritious diet, eliminating smoking, maintaining a healthy body weight, performing some amount of exercise, reducing bad cholesterol levels, monitoring stress levels and controlling diabetes and high blood pressure. If the condition is assesed and considered incapable of being rectified then a heart transplant may have to be carried out.