Coronary Heart Disease
Definition of Coronary Heart Disease
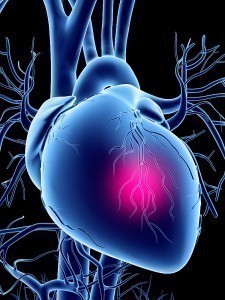
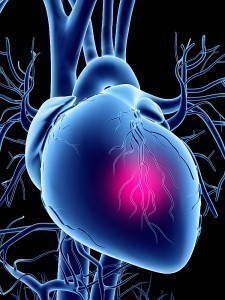
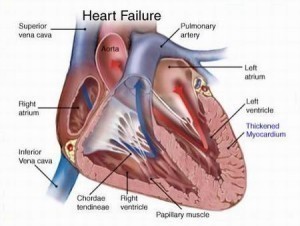
The heart muscle or the myocardium gets its supply of oxygen and nutrients to pump blood through arteries called the coronary arteries. When these arteries get blocked due to the accumulation of calcium, fat or plaque, it results in the obstruction of the flow of nutrients. The arteries tend to become narrow and as a result, the heart does not get sufficient amount of blood. This leads to Coronary Heart Disease or CHD. It is a fast becoming a major cause of death in the United States of America and many other countries in the world.
Causes of Coronary Heart Disease
There are several causes that could result in an individual developing Coronary Heart Disease. They include:
- Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis is a condition where there is an accumulation of atheromatous plaque in the coronary arteries. This results in the lack of sufficient flow of blood. This condition is called Ischemia. Coronary Heart Disease is sometimes referred to as Ischemic Heart Disease also.
- Smoking: Smoking or use of tobacco in any form, is one of the causes of CHD. It is therefore, advisable to work towards the cessation of this habit with the help of a medical practitioner.
- Heredity: CHD can be caused because it runs in the family. Regular health checks can therefore prove to be timely in detecting the disease.
- High Cholesterol: When there is an increase in the level of bad cholesterol (LDL – Low-Density Lipoprotein) and a fall in the level of good cholesterol (HDL- High-Density Lipoprotein), it could lead to Coronary Heart Disease.
Other causes include:
Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease
As the heart does not receive the required amounts of nutrients or blood due to the blocked coronary arteries, the body registers this impairment and indicates that there is a problem through the following symptoms.
- a general feeling of discomfort
- shortness of breath due to exertion
- being unable to sleep without being propped up by two pillows or more
- irregular heartbeat
- fatigue
- heart palpitations
- chest pain (Angina Pectoris) which will discontinue after resting
- pain in the jaw, shoulder blades and left arm that is felt after exercise or while resting
- feeling dizzy and light-headed
- fainting
- cardiac arrest – this could either be the first instance of coronary heart disease or it could occur because a person has already suffered from a heart attack
Treatment for Coronary Heart Disease
Medical Treatment
- Beta-blockers: Beta-blockers serve the purpose of reducing the patient’s blood pressure and heart rate. In other words, they help to reduce the heart’s demand for oxygen.
- Calcium channel blockers: Calcium channel blockers contribute to dilate the coronary arteries. This helps to improve the blood flow. They also help to reduce blood pressure and slow the heart rate.
- Statins: As mentioned earlier, an increase in the levels of bad cholesterol in the blood is a possible cause for Coronary Heart Disease. Statin drugs help to lower the level of cholesterol. They aid in slowing down the progress of CHD and sometimes, help in preventing a second attack.
- Nitroglycerin: Nitroglycerin are time-tested medicines that play the role of a vasodilator (widening of blood vessels). They come in the form of sprays, patches or tablets.
Invasive Procedures to Treat Coronary Heart Disease
- Coronary Angioplasty: This serves a dual purpose. It is used for both treatment and diagnostic purposes. It is a minimally invasive procedure which, simply put, tries to flatten the accumulated plaque against the walls of the artery. This helps to increase the flow of blood through the arteries.
- Brachytherapy: refers to the usage of radiation to help clear blockages to facilitate treatment of Coronary Heart Disease.
- Atherectomy: minimally invasive surgical procedure that aims to fight atherosclerosis.
- Surgery: When minimal invasive treatment fails to cure, improve or stabilize the patient’s condition, surgery is considered to be the best option.
Lifestyle Changes that help to Inhibit Progress of Coronary Heart Disease
The following lifestyle changes will also play a very significant role in inhibiting the progress of Coronary Heart Disease.
- quit smoking
- start an exercise routine
- work towards a healthy diet
- work towards maintaining a healthy body weight
- taking medicine to lower high cholesterol levels
- taking medication as per medical practitioner’s advice to control diabetes and high blood pressure
- consciously work towards reducing stress levels
For more information on Coronary Heart Disease read:
Coronary Heart Disease?
Coronary Heart DiseaseCoronary Heart DiseaseCoronary Heart DiseaseCoronary Heart Disease