E Coli Symptoms
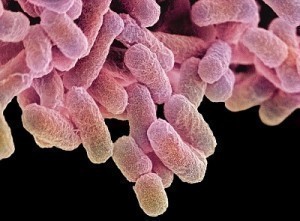
E. coli, which stands for Escherichia coli, is classified as a Gram-negative bacterium that affects the lower intestine, usually of warm-blooded organisms. Some of its strains pose grave threat to human health as they can lead to food poisoning. For instance, the so-called E. coli O157:H7 causes severe symptoms like painful abdominal cramps and bloody diarrhea. When left untreated, these signs can lead to life-threatening medical conditions such as hemolytic uremic syndrome. Here is a quick take on the different major and minor E. coli symptoms including the possible diagnostic procedures and treatments.
Signs of E. Coli
In the early stages, the symptoms of this infection are hard to notice. However, these signs will make life more difficult for patients three to four days after acquiring the disease. Within a week, these symptoms are expected to blossom fully. One of the major signs is diarrhea, which usually ranges from mild to severe cases. Meanwhile, sufferers of this condition can expect tenderness, sharp pain and cramping somewhere in the abdominal area. Moreover, they are likely to experience vomiting and nausea.
In case the major symptoms of the infection arise, patients are highly advised to consult doctors right away. These cases include bloody diarrhea, severe or persistent diarrhea as well as feeling ill after eating undercooked ground beef.
E. Coli Diagnosis
Diagnosis is a very important part of the treatment process for E. coli. By undergoing a series of diagnostic examinations, physicians can point out the real cause of this serious medical condition. It is also possible to rule out other possibilities. Patients must submit stool samples for analysis. This will help confirm the presence of E. coli or other factors that are producing the different symptoms. The proper and immediate diagnosis of the condition is highly important especially to prevent the worsening of infection.
E. Coli Treatment
When treating this type of infection, it is not advisable to take anti-diarrheal medications because such drugs can actually prevent the human body from eliminating toxins. Of course, the intake of antibiotics is necessary to treat the infection. However, some of these drugs are not effective against this type of disease. One of the highly trusted antibiotics against this type of infection is amoxicillin.
In addition, patients can also take other efficient antibiotics like aminoglycosides, nitrofurantoin and ciprofloxacin. Other possible options include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, aztreonam, carbapenems and cephalosporins. In some places, phage therapy is recommended for this disease, especially in Poland and in the Republic of Georgia.