Eczema Treatment
What we often call eczema is also known as atopic dermatitis. It is a skin disease that is long lasting or chronic. The term atopic basically means something which is inherited while dermatitis means a skin inflammation. Those who suffer from atopic dermatitis have skins that become very itchy. A patient’s skin is usually marked by scaling, crusting, reddening, swelling, and weeping with a clear fluid. Understanding it is also the key to finding the proper eczema treatment.
Types of Eczema
The term eczema is usually used to describe other skin inflammations. However, atopic dermatitis is the most common type of inflammation among many. Some of the different types of dermatitis even have the very similar symptoms. Here are the skin diseases that we call eczema.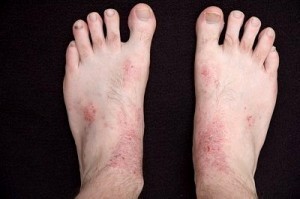
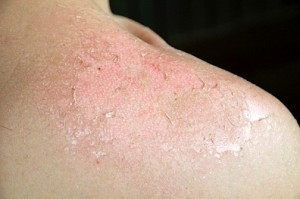
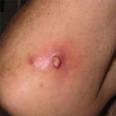
Atopic Dermatitis: chronic skin disease that is often characterized by inflamed and itchy skin.
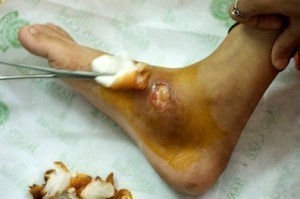
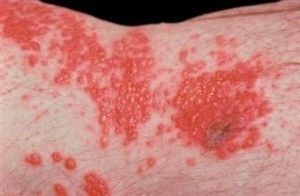
Allergic Contact Eczema: skin disease where the skin reacts to foreign substances it comes in contact with. Examples of such substances include preservatives found in lotions and creams and poison ivy. The skin is characterized by an itchy, red, weepy reaction.
Contact Eczema: comparably similar to Allergic Contact Eczema, except that the symptoms are localized to a certain area of the skin. This type of eczema is usually caused by an allergy causing substance.
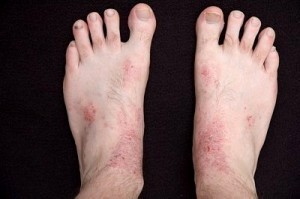
Dyshidrotic Eczema: symptoms involve skin irritations on both palms and soles of the feet. Deep, itching, burning, and clear blisters usually form.
Neurodermatitis: characteristic symptoms include scaly patches formed on lower legs, wrists, head, or forearms but is only localized to a certain area. The patches appear like insect bites.
Numular Eczema: characterized by irritated skin patches that are coin-shaped. These patches are usually found on the buttocks, lower legs, back, and arms. They are usually scaly and crusted and will feel very itchy.
Seborrheic Eczema: characterized by yellow, scaly, oily patches of skin usually located on a person’s scalp and face.
Stasis Dermatitis: this condition is generally related to a circulatory problem and is characterized by skin irritations on the person’s lower legs.
Causes of Eczema
In order to correctly ascertain the proper eczema treatment for a specific type of dermatitis one has to understand its causes. Unfortunately, the exact cause of eczema is not yet known. However, it is found out that this disease is the result of a combination of environmental and genetic factors.
It is found that children are more prone to this disease. Furthermore, the likelihood of a child getting it increases if both of the child’s parents have atopic diseases. About 50% of children who develop this disease eventually develop either asthma or hay fever. The clue in eczema treatment comes in both the hereditary and environmental factors that bring about its symptoms.
Stress does not cause atopic dermatitis. However, it can worsen the condition. It is also known that the disease is related to the malfunction of a person’s immune system and thus leading to symptomatic allergic reactions.
Common Irritants
Since environmental conditions affect the development of this disease, it is important to know what common irritants serve as triggers. Some of these common irritants that patients should avoid include cigarette smoke, dust and sand, solvents, mineral oils, chlorine, some cosmetics and perfumes, detergents and soaps, synthetic fibers, and wool.
Minor and Major Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms is necessary in eczema treatment, which is also true for any other disease for that matter. Some of the minor symptoms of this disease include drying of skin accompanied by rough bumps and patchy scales, inflammation around the lips, susceptibility to skin infection, high levels of igE (immunoglobulin E), nipple eczema, and positive skin allergy tests.
Major symptoms that should be noted for proper eczema treatment include intense itching, recurring symptoms, chronic symptoms, and rashes that are typical to the different types of eczema found in characteristic locations. Another important major factor to look into is either a family or personal history of atopic disorders, which includes asthma, hay fever, and different forms of eczema.
Eczema Treatments
Doctors will usually prepare and recommend a treatment plan. This plan is based on a patient’s general health, age, and symptoms. This treatment will be more effective if family members, the patient, and doctor work together as a developed partnership. The family members who provide care will play a major role in the success of the treatment.
Part of the treatment will involve skin care routines. The patient must avoid contact with any substance that may trigger skin irritations or the immune system. Both the patient and immediate family members concerned should notify the doctor of the patient’s response to treatment.
Medications will be helpful in eczema treatment. Immunomodulators help control and reduce skin inflammation. They also reduce the amount of reaction coming from the immune system when medications are applied to the skin. Other medications also reduce flares and help maintain skin texture.
Corticosteroid ointments and creams will also be used. At times, your doctor may prescribe over the counter preparations, but more often than not, stronger corticosteroid creams will be used as medication. Systematic corticosteroids will only be prescribed when creams and topical treatments are ineffective. These can either be oral medications or injected. Antibiotics will be prescribed to treat skin infections, which are taken by mouth or applied as an ointment.
Antihistamines may also be prescribed. Some of these antihistamines may cause drowsiness at night, which helps the patient gain restful sleep. Adult patients may be prescribed with medication that suppress the immune system when the case is severe. Rarely would a patient be hospitalized for eczema treatment. Doctors may also opt for phototherapy procedures for mild to moderate cases in adults and older children.