Hashimoto’s Disease
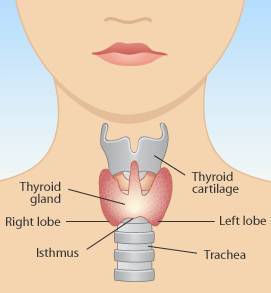
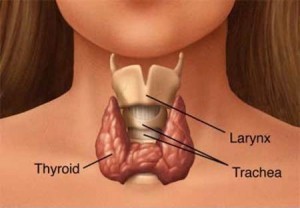
This disease refers to any problem related to the thyroid glands located in the back of the neck. With Hashimoto’s Diseases the body recognized the thyroid as being foreign and the immune system will attack it, resulting in it being irritated. This attack on the thyroid gland leads to an underactive thyroid gland, noted as being Hypothyroidsm. The thyroid gland produces the Pituitary Thyroid Hormone which is responsible for controlling how the body uses it energy and also influences growth. Hashimoto’s Disease can affect anyone; however it is common in women between the ages of 30 and 50.
Cause of Hashimoto’s Disease
Hashimoto’s Disease is hereditary (genetics) , and may be caused even in persons whose family members had other thyroid diseases.
Symptoms of Hashimoto’s Disease
The signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism vary widely, depending on the severity of hormone deficiency. However these listed here are some of the more common symptoms of the disease.
- have a feeling of fullness or tightness in the throat.
- trouble swallowing food or liquids.
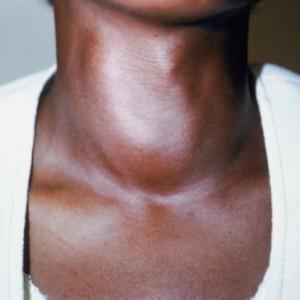
- a swelling or bump (called a goiter) in the front of the neck.
- experience
- forgetfulness,
- depression,
- coarse dry skin,
- slow heartbeat,
- weight gain,
- constipation
- tiredness
Many people who have Hashimoto’s Disease show no visible symptoms at all. However an ordinary blood test would show that the thyroid hormones are out of balance.
Treatment of Hashimoto’s Disease
There is no cure for Hashimoto’s Disease at present, however there are treatments available now that can stop the long terms effects of an underactive thyroid. Thyroid medication can be taken orally to replace the hormones that are normally produced by the thyroid. These medications may be taken for an extended period of time depending on the blood test results. There is constant monitoring of patient who are being treated with hormone therapy so as to not have the levels of this hormones get too high in the body as it known to speed up osteoporosis.