Myocardial Ischemia Symptoms
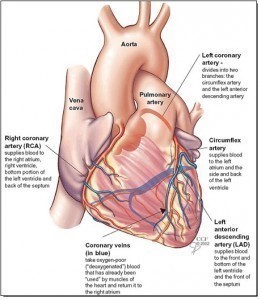
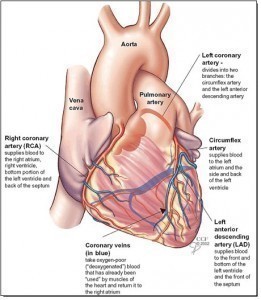
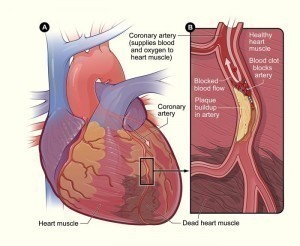
Myocardial ischemia is an ischemic disease involving reduced blood supply to the heart. The most common cause for this condition is coronary heart disease mostly involving the hardening of the blood vessel walls due to plaque build ups resulting to a condition called as atherosclerosis.
Other predisposing factors that can cause myocardial ischemia symptoms to occur are medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia where there is increased level of cholesterol and hypertension caused by high level of blood pressure. Smoking also plays a role in the development of myocardial ischemia.
Identification of the common myocardial ischemia symptoms is necessary in order to obtain preventive measures that can predispose one to sustain a more serious complication of heart diseases that may lead to stroke, cardiac arrest or death.
Myocardial Ischemia Signs and Symptoms
There are different kinds of manifested myocardial ischemia symptoms according to the extent of blockage of blood supply to the heart. Minor myocardial ischemia may involve mild symptoms of angina or chest pain with decrease level of tolerance to exercise or rigorous activities.
Major myocardial ischemia symptoms usually involve a sudden cardiac arrest or arrhythmia where there is an abnormal heart rhythm. The person may also faint and in major cases, the attack may lead to a sudden death.
Common warning signs of myocardial ischemia symptoms typically involve a pain in the nape or jaw, chest pain, sweating or clammy skin, pain in the arm, vomiting, nausea and shortness of breath. In diabetic individuals the myocardial ischemia symptoms are often not evident.
Myocardial Ischemia Symptoms Diagnosis
Establishing a diagnosis for myocardial ischemia symptoms usually involves basic laboratory tests to determine whether the symptoms are due to ischemia of the heart. This usually involves electrocardiogram, chest x-rays, coronary angiogram, and blood tests. These are complimentary diagnostic tools along with the thorough medical examination and medical history carried out by a physician. The patient is also subject to cardiac stress test.
The physician will often rule out other possible conditions that may mimic the myocardial ischemia symptoms and to establish other differential diagnosis. The risk factors that may predispose one to the myocardial ischemia symptoms are also explored and addressed including family history, history for smoking, high cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle, hypertension and diabetes.
Making a diagnosis of the myocardial ischemia symptoms will also involve diagnosing whether the patient experiences stable angina where chest pain is only present during exertion or activities. Unstable angina is one where chest pain occurs even at rest.
Myocardial Ischemia Treatment
Prevention against the myocardial ischemia symptoms remains to be the best treatment. Common preventive measures involve controlling cholesterol level, active lifestyle, eating nutritious foods, avoid smoking and exercise.
Medication is the first line of treatment option for the management of myocardial ischemia symptoms. Stable angina is treatable with antianginal drugs that can reduce the occurrence of chest pain.
Other medications prescribed for myocardial ischemia symptoms are beta blockers, thrombolytic agents and nitrates. Other treatment options involve invasive procedures such as angioplasty and coronary artery bypass surgery. Modification of lifestyle risk factors is also helpful.