Prostate Disease
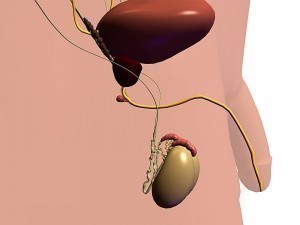
The prostate is a small gland in the male reproductive system. As some males age this gland may start to have disruptions in its normal functioning; disruptions ranging from urinary problems to potentially life threatening cancer. As the male gets older the prostate naturally gets larger due to the presence of a particular hormone in the body. Prostate disease normally affects men over the age of 50, although some men may experience prostate problem at a younger age, as early as the mid 20s. Now prostate disease can be one of three
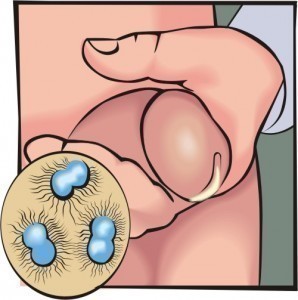
- Prostatitis ( inflammation of the prostate), which speaks to an infection of the prostate, this infection may be bacterial in nature
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia ( noncancerous enlargement of the prostate)
- Prostatic Carcinoma (prostate cancer)
Symptoms of Prostatitis
- Painful/difficult urination
- Fever
It is often believed that once there is a disorder/disease of the prostate that one will suffer with an erectile dysfunction.
Symptoms of Benign Hyperplasia
- Painful/difficult urination
- Painful/burning whilst ejaculation
- Frequent urination, especially at night time
- Difficulty in having an erection
- Frequent pain or stiffness in lower back, hips, or upper thighs
- Inability to urinate, or
- Dribbling of urine
Symptoms of Prostatic Carcinoma
- Blood in urine or semen.
- A frequent need to urinate, especially at night.
- A painful or burning sensation during urination or ejaculation.
- Difficulty starting or stopping the urinary stream.
- A weak or interrupted urinary stream.
Causes of Prostatitis
Prostatitis is caused primarily by bacterial infections; however this disease has some inheritance trait to it.
Causes of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The causes of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia are still unknown; however it is believed to be tied to the male hormone testosterone and also due the genetic traits.
Causes of Prostatic Carcinoma
This is caused primarily by two factor, these are:
- Genetic
- Diet
Treatment for Prostatitis
Treatment for prostatitis is a prescription for antibiotics by mouth. Home care includes drinking plenty of fluids, medications for pain control, and rest.
Treatment of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The treatment for this disease can be separated into two categories lifestyle and medication.
Lifestyle- patients are to moderate the levels of alcohol, caffeine entering the body, and also to avid fluid intake before sleeping.
Medications- two medications can be used;
- Alpha blockers, which serves to decrease the blocking of the flow of urine.
- 5?-reductase inhibitors, which serves to prevent he prostate from enlarging naturally.
Treatment of Prostatic Carcinoma
The treatment for prostate cancer varies with every man depending on the specifics of his case. There are three basis treatment options available, these are
- Surgery to remove the prostate
- Radiation to kill cancer cell, and
- Active surveillance/expectant management.
As the cancer progresses these treatment options may not be enough to adequately fight off the cancer, so then hormonal therapy may be used.
In cases where treatment is done and the cancer re-occurs then chemotherapy may be used to help kill the cancer cells.
For more information on Prostate Disease read: