Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
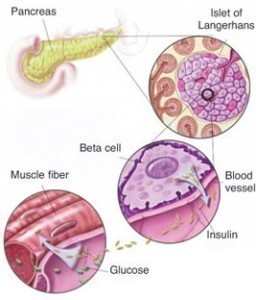
Known as a medical term used to refer to a health condition in which the body produces lower than the required blood glucose, hypoglycemia has different symptoms but all these lead to neuroglycopenia. The after effects of this condition include unconsciousness, seizures, death as well as permanent brain damage. To prevent these effects, it is important that patients know the early, minor and major symptoms of hypoglycemia. In addition to these, it is very beneficial if they have ideas about the proper diagnosis and treatments for this health condition.
Hypoglycemia Signs
The symptoms of hypoglycemia can be categorized into three types, namely adrenergic manifestations, glucagon manifestations and neuroglycopenic manifestations. The major adrenergic signs include palpitations, dilated pupils, parasthaesia, anxiety and nervousness. The minor glucagon symptoms are headache, nausea and hunger. The major neuroglycopenic manifestations include impaired judgment, depression, negativism, personal change and daydreaming. Aside from these, the neuroglycopenic symptoms include stupor, abnormal breathing, focal seizures, amnesia, dizziness, delirium, slurred speech, ataxia and fatigue.
Hypoglycemia Diagnosis
To have ideas about the effective treatments that patients with hypoglycemia should take, it is important to let physicians perform diagnostic tests in order to examine the real cause of this illness. One of the most useful and efficient diagnostic tests used by health professionals to know the underlying cause is known as circumstance. In this test, physicians interview their patients. They ask several questions about the medical history of patients. The questions may include the patient’s age, time of their last meal as well as the overall health status.
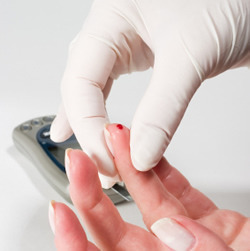
Another diagnostic method that can be used is blood test. To identify if a patient is suffering from this disease, medical technologists will take blood sample during an episode of hypoglycemia and several hours after the episode. In minor cases, physicians commonly perform diet experimentation to identify the true cause of the illness.
Hypoglycemia Treatment
To treat acute condition, patients should drink fluids or eat foods that have high sugar content to reach the required level of blood sugar. Treatments for severe symptoms of the disease include the use of insulin and the use of intravenous glucose. Aside from these, patients who experience the early symptoms of hypoglycemia can try oral intake of glucose to treat the condition. Most physicians advise patients with chronic condition to have their own glucagon emergency rescue kit, which include a standard adult dose of glucagon as well as a syringe and small vials that they can use to regulate the level of blood sugar.