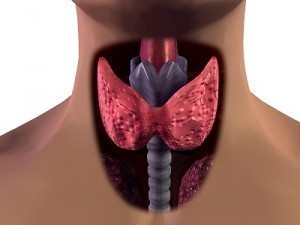
Thyroid Disease
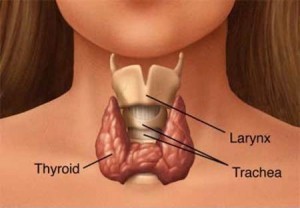
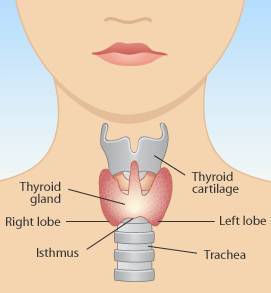
Thyroid disease refers specifically to any disease that interferes with the functioning of the thyroid. Thyroid disease may be categorized into four major types: Hyperthyroidism: having too much thyroid hormone; Hypothyroidism: having too little thyroid hormone; Benign thyroid conditions which usually involve small harmless growths on the thyroid and cancer of the thyroid.
Causes of Thyroid Disease
The causes of thyroid disease will depend on the type of thyroid disease.
Hypothyroidism is primarily caused by iodine deficiency. Iodine deficiency may manifest as a result of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an insufficiency of hormones from the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland or a defective thyroid gland or having no thyroid gland. It can also be a result of developing a postpartum condition specifically postpartum thyroiditis which affects 5% of women up to a year after giving birth. It is also possible to develop the condition as the result of sporadic inheritance or a genetic mutation. Hypothyroidism affects an estimated 3% of the world’s population.
Hyperthyroidism may be caused by three distinct clinical conditions specifically: grave’s disease, toxic multinodular goitre or toxic thyroid adenoma. It is also possible to be afflicted with this condition because of thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid), consuming excessive amounts of thyroid hormone, suffering from postpartum thyroiditis or taking courses of the anti-arrhythmic drug Amiodarone.
The cause of thyroid cancer has not yet been discovered. However, risk factors such as advanced age (being over 40), being a woman (women are 3 times more likely to be affected by this condition), having a family history of thyroid cancer, iodine deficiency or being exposed to radiation at some point may increase a person’s probability of developing the condition.
Symptoms of Thyroid Disease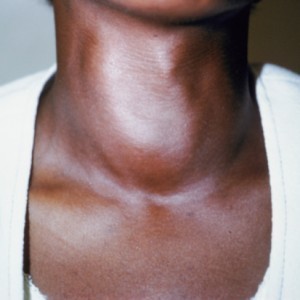
The symptoms of the disease will be related to the specific condition.
- Hypothyroidism
- Early Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Cold Intolerance (decreased ability to endure cold conditions)
- Depression
- Thin, easily broken fingernails
- Thin, brittle hair
- Paleness
- Poor muscle tone
- Joint pain and muscle cramps
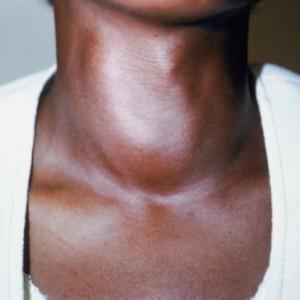
- Goiter
- Constipation
- Bradycardia (low heart rate)
- Dry, itchy skin
- Weight gain and water retention
- Decreased sweating
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Late symptoms
- Dry puffy skin, usually on the face
- Thinning of the outer portion of the eyebrows
- Low basal body temperature
- Slow speech and hoarseness of the voice
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
- Anxiety
- Heat intolerance
- Hair loss
- Hyperactivity
- Irritability
- Depression
- Apathy
- Poluria
- Heart Palpitations
- Weight loss
- Delirium
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Loss of libido
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Some Neurological Symptoms
- Myopathy
- Tremors
- Chorea
- Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
- A nodule in the neck just about the thyroid region
Treatment of Thyroid disease
The treatment will be related to the type of thyroid condition.
Hypothyroidism is treated by administering thyroid hormone which may be synthetic or animal based. This will be used to re-build thyroid levels.
Hyperthyroidism will be treated with medication to suppress thyroid activity and may also include surgery. Radiodine or removing part or all of the thyroid are two common methods of treating the disease.
Thyroid cancer may be treated with thyroxine therapy if the cancer is benign or with surgery if the tumour is malignant.
Additional Reading on Thyroid Disease