Treatment for Gout
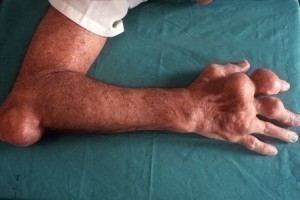
Gout is one of the most painful kinds of arthritis anyone can ever endure. It usually occurs when someone’s body has accumulated too much uric acid. This increased build up has several effects. Some of these effects include lumps on the skin, kidney stones, and uric acid deposits formed in the big toe. Due to the pain they experience, people look for a treatment for gout just to relieve the symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms of Gout
The most common sign of acute gout is found on a patient’s big toe usually at the base. This part of the big toe is usually inflamed. There are also other joints that can be affected by gout. These include elbows, fingers, wrists, knees, and ankles. Acute attacks often begin with a fast inception of pain. It is then followed by swelling, reddish discoloration, warmth, and marked tenderness.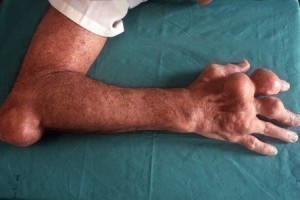
That part of the body would be so tender that even a slight touch can be quite unbearable. The attacks of pain usually take several hours to subside. Some even lasts for several days. The majority of gout patients will experience repeated attacks as years go by.
Treatment for Gout
There are a couple of things one needs to understand regarding the treatment. The first part of gout treatment is to address the inflammation of the affected joints. The next part of the treatment process is long-term management of this disease. The goal is to address the immediate symptoms and to prevent any future attacks of this kind of arthritis. Another objective of treatment for gout is to shrink the crystal deposits.
One part of the treatment for gout entails reducing the inflammation that occurs. Doctors often prescribe medication to do this. Of course, prevention of future attacks is just as important as treating the current discomfort and other symptoms brought about by this condition.
The preventive treatment for gout includes making dietary changes and taking in prescribed medication. Some of the things one can do to prevent gout attacks in the long run include maintaining or increasing the amount of fluid intake, reducing alcohol consumption, and weight reduction.
Making adjustments in one’s diet reduces the amount of uric acid levels in the patient’s blood. This means that patients should reduce the amount of purine-rich food they eat. Examples of this kind of food include organ meat (e.g. kidneys, liver, and brain), sweetbreads, and shellfish. There is a correlation between the increase in the amount of seafood and meat intake with the increased risk of gout attacks.
Medications used in gout treatment include pain relievers, anti-inflammatory agents, corticosteroids, and colchicine. Colchicine and corticosteroids decrease the amount of inflammation. The last bit of medication for gout treatment is medication that manages and addresses the underlying metabolic derangement.