What Causes Atypical Squamous Cells?
Atypical Squamous Cells (ASC) refers to an unclear result from a pap smear that requires a repeat pap smear. This may be due to several factors such as use of medication that may interfere with the results of the test, an infection such as herpes, HPV or Candida, or the cells used for the test were not the right amounts.
Causes
When a woman goes in to do a pap smear the result of the test may show that the squamous cells are not normal in appearance which means it may be precancerous. Further tests will need to be done in order to verify this.
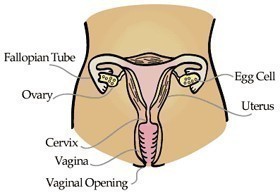
Squamous cells make up the outer layer of the vagina and cervix. Cells that appear somewhat abnormal are seen result from squamous intraepithelial lesions. A woman who has been diagnosed with ASC will need to be tested further as there is the likelihood that she may have a precancerous lesion. This occurrence is common in 5 to 17 percent of women.
 ASC is split into atypical squamous cells of undetermined importance (ASC-US) and atypical squamous cells will not be able to eliminate high grade lesion (ASC-H). Women who are older than 20 years old can get their ASC –US result evaluated in three ways:
ASC is split into atypical squamous cells of undetermined importance (ASC-US) and atypical squamous cells will not be able to eliminate high grade lesion (ASC-H). Women who are older than 20 years old can get their ASC –US result evaluated in three ways:
- HPV testing – This type of testing is done following an ASC-US and it can be done while the cervical cytology is being done. The convenience of this is that the woman does not have to return for a second visit. A woman who was tested positive for high risk HPV will need to have a Colposcopy done as the risk of having precancerous lesions is very great. On the other hand, a woman who has tested negative is unlikely to have cervical pre-cancer. A repeat cervical cytology will need to be done however, within a year. It is noticed too that in many cases the ASC –US resolves during this time.
- The cervical cytology should be repeated within 6 month’s time. Where the test is normal, another round of test must be done in 6 month’s time until there are two normal tests in succession; routine screening should follow after this. Colposcopy is only recommended if the woman‘s second ASC –US result shows an abnormality or if other chronic abnormality occurs.
- Have Colposcopy done – A Colposcopy is a procedure that is done in a doctor’s office where the clinician performs a close and thorough examination of the cervix following an abnormal pap smear.
ASC-H has a greater chance of causing precancerous change than ASC-US. Further evaluation with Colposcopy will be required in this case.
The management and evaluation of pregnant women is different from non-pregnant women because of the risk that trauma to the cervix could result in preterm labor or delivery.
For women age 20 years and younger, abnormal cervical cytology is often treated differently as, in this age group, there is a good chance that the abnormal area will resolve over time, without treatment. Although there is a high rate of HPV infection in this group, there is a very low rate of cervical cancer.

I had a pap and it came back with no HPV or cancer but I have atypical squamous cells. I need to repeat my pap in 6 months. What causes atypical squamous cells to appear in a pap?
Thanks, Sharon