What Causes Conductive Hearing Loss?
Definition
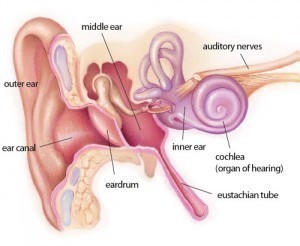
Conductive hearing loss happens when there is a problem conducting sound wave through the outer ear, tympani membrane (eardrum) or middle ear (ossciles). This type of hearing may occur in conjunction with sensorineural hearing loss or alone.
External ear some common causes are cerumen (earwax) and otitis external
Earwax (also called cerumen) blockage is common. A doctor can cure this easily by removing the wax either with specially designed instruments or by flushing with water. There are many over-the-counter wax control preparations that can be used at home. However, they sometimes can cause external ear infections.
Otitis External, this is a painful outer ear infection. Treatment often requires antibiotics.
External ear some uncommon causes are foreign bodies in the external auditory canal, exostoses, and tumors of the canal
Foreign bodies include small things like pebbles, insects, beans, etc. These can be immensely troublesome because their removal can be difficult, and infections are common. These are most easily removed using an examining microscope, but in some instances, surgical removal is needed.
Exostosis is the overgrowth of outer ear canal bone. This is the body’s way of protecting the ear drum from the frequent rush of cold water against it which commonly occurs with surfing. They develop over many years and result in infections, pain, plugging and hearing loss.
Tumors can affect the inner ear. They are very rare. The most common ones are cholesteatoma associated with chronic ear infection (it is not a true tumor) and glomus tumor.
Middle ear, common causes otitis media and tympani membrane perforation
Otitis media: This is very common. Fluid buildup in the middle ear generally is organized under the term otitis media. In general, the treatment is to get rid of the fluid.
Perforated eardrum is a rupture or perforation of the ear drum which can occur as a result of infection, trauma (e.g. by trying to clean the ear with sharp instruments), explosion, loud noise or surgery (accidental creation of a rupture). Flying with a severe cold can also cause perforation due to changes in air pressure and blocked Eustachian tubes resulting from the cold. This is especially true on landing.
Middle ear uncommon causes cholesteatoma, ostosclerosis
Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear.
Otosclerosis is an abnormal growth of bone near the middle ear.
Inner ear common causes
Severe Otosclerosis, form of mechanical conductive hearing loss most commonly found in people who have been subjected to intense noise. This will occurs when there is an obstruction in either the oval window and/or the round window. This type of hearing loss can usually be repaired by surgical opening of the blockage.
Inner ear uncommon causes
Superior canal dehiscence syndrome is a rare medical condition of the inner ear, leading to hearing and balance disorders in those who are affected. The symptoms are caused by a thinning or complete absence of the part of the temporal bone overlying the superior semicircular canal of the vestibular system. This may result from slow erosion of the bone or physical trauma to the skull and there is evidence that the defect or susceptibility is congenital.
For more information on What Causes Conductive Hearing Loss read: